Improving Breed Standards through Selective Breeding
Selective breeding is a powerful tool that has been utilized for centuries to improve the breed standards of various animal species. By carefully choosing which individuals to reproduce based on desirable traits, breeders can enhance specific characteristics within a population over time. This selective process has been instrumental in shaping the appearance, temperament, and health of many domesticated animals, including dogs, cats, horses, and livestock. In this article, we will explore the importance of improving breed standards through selective breeding and the impact it has on the overall well-being of animal populations.
**The Art of Selective Breeding**
Selective breeding, also known as artificial selection, involves intentionally mating animals with the goal of producing offspring with desired traits. This process relies on the principles of genetics and inheritance, where specific genes responsible for certain characteristics are passed down from parents to their offspring. By selecting breeding pairs that exhibit the desired traits, breeders can increase the likelihood of those traits being expressed in future generations.
**Enhancing Desired Characteristics**
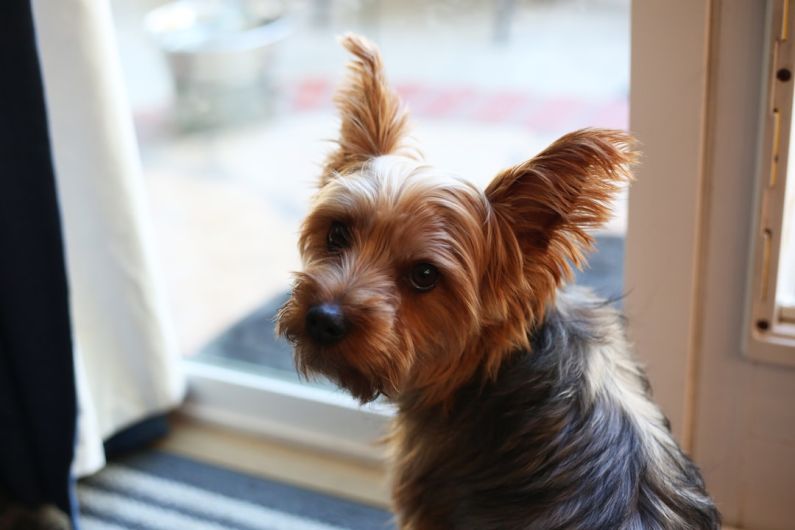
One of the primary objectives of selective breeding is to enhance desired characteristics within a breed. For example, in dog breeding, breed standards outline the ideal physical and behavioral traits for each breed. By selectively breeding dogs that conform to these standards, breeders can work towards producing offspring that meet the desired criteria. This can result in improvements in coat color and texture, body conformation, size, and temperament.
**Ensuring Health and Longevity**
Selective breeding also plays a crucial role in improving the overall health and longevity of animal populations. By selectively breeding for traits associated with good health, such as resistance to certain diseases or genetic disorders, breeders can help reduce the incidence of hereditary health issues within a breed. Additionally, breeding for longevity can result in animals that live longer, healthier lives, benefiting both the animals themselves and their owners.
**Preserving Genetic Diversity**
While selective breeding focuses on enhancing specific traits, it is also important to consider the preservation of genetic diversity within a breed. Genetic diversity is essential for maintaining a healthy population, as it provides the variability needed to adapt to changing environments and resist potential threats such as diseases. Breeders must carefully manage selective breeding programs to avoid excessive inbreeding, which can lead to genetic disorders and reduced overall fitness in a population.
**Challenges and Ethical Considerations**
Despite its benefits, selective breeding also poses challenges and ethical considerations that breeders must navigate. One of the main challenges is balancing the pursuit of certain traits with the maintenance of overall breed health and genetic diversity. Breeders must make informed decisions about which traits to prioritize and consider the potential consequences of intense selection for specific characteristics.
Additionally, ethical considerations come into play when breeding animals for specific traits that may impact their well-being. For example, extreme conformation standards in certain dog breeds can lead to health issues such as breathing difficulties, joint problems, and other physical ailments. It is essential for breeders to prioritize the health and welfare of the animals they are breeding and to avoid perpetuating traits that compromise their well-being.
**Future Directions in Selective Breeding**
As our understanding of genetics and animal breeding continues to advance, so too does the potential for improving breed standards through selective breeding. Emerging technologies such as genomics and assisted reproductive techniques offer new opportunities for breeders to make more informed breeding decisions and accelerate genetic progress within populations. By harnessing these tools responsibly, breeders can continue to enhance breed standards while prioritizing the health, diversity, and welfare of the animals they work with.
**In Summary**
Improving breed standards through selective breeding is a dynamic and ongoing process that requires careful consideration of genetic principles, breed standards, health, and welfare considerations. By selectively breeding for desired traits, breeders can enhance characteristics such as appearance, temperament, and health within animal populations. However, it is essential for breeders to balance the pursuit of specific traits with the maintenance of genetic diversity and overall breed health. Through responsible breeding practices and a commitment to animal welfare, breeders can continue to make strides in improving breed standards and ensuring the well-being of domesticated animal populations.